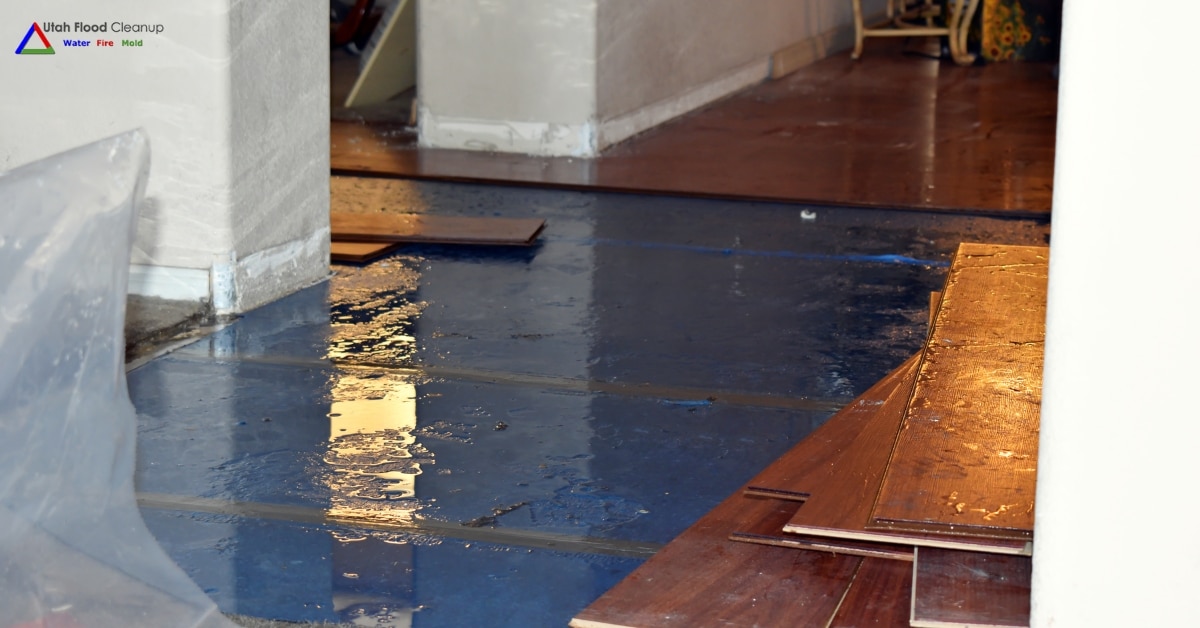
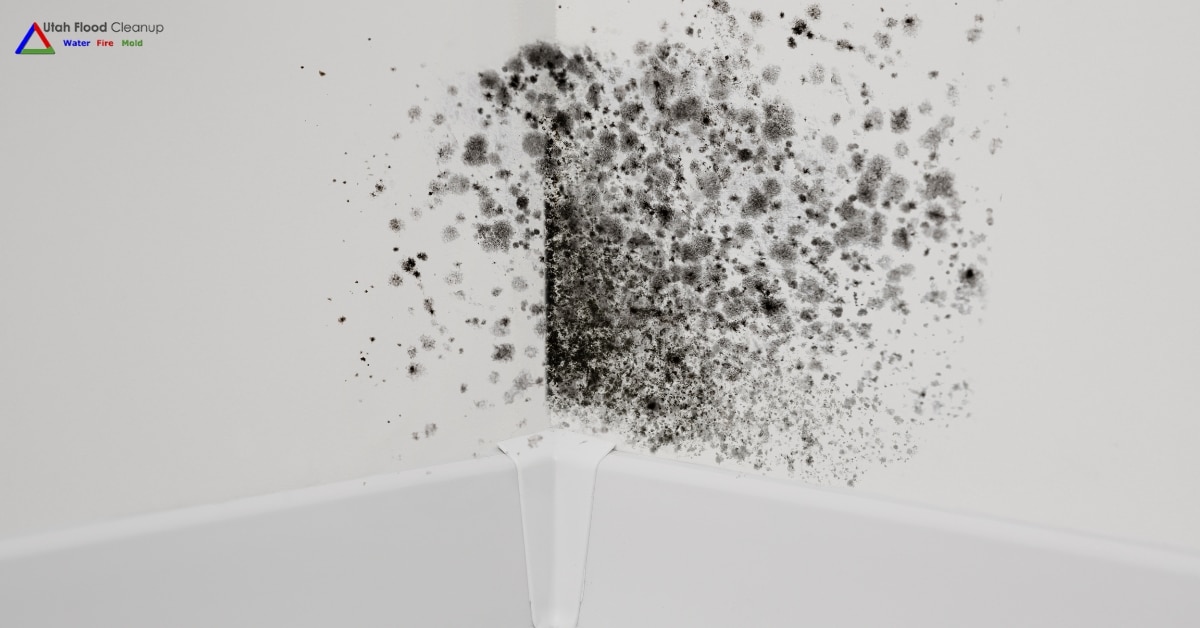
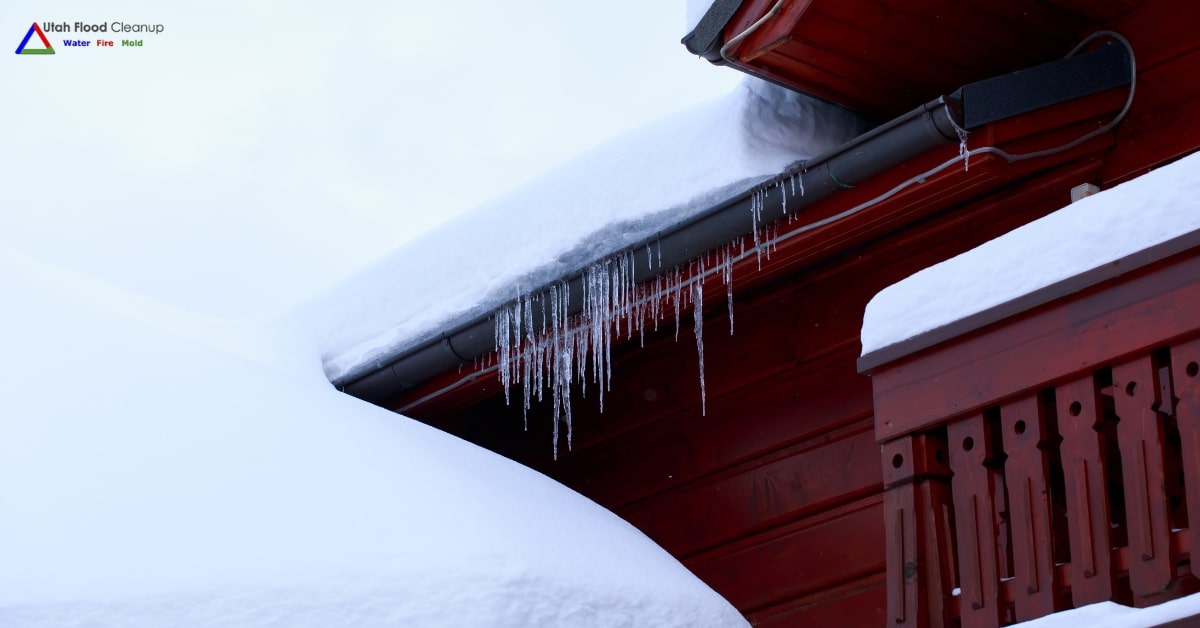
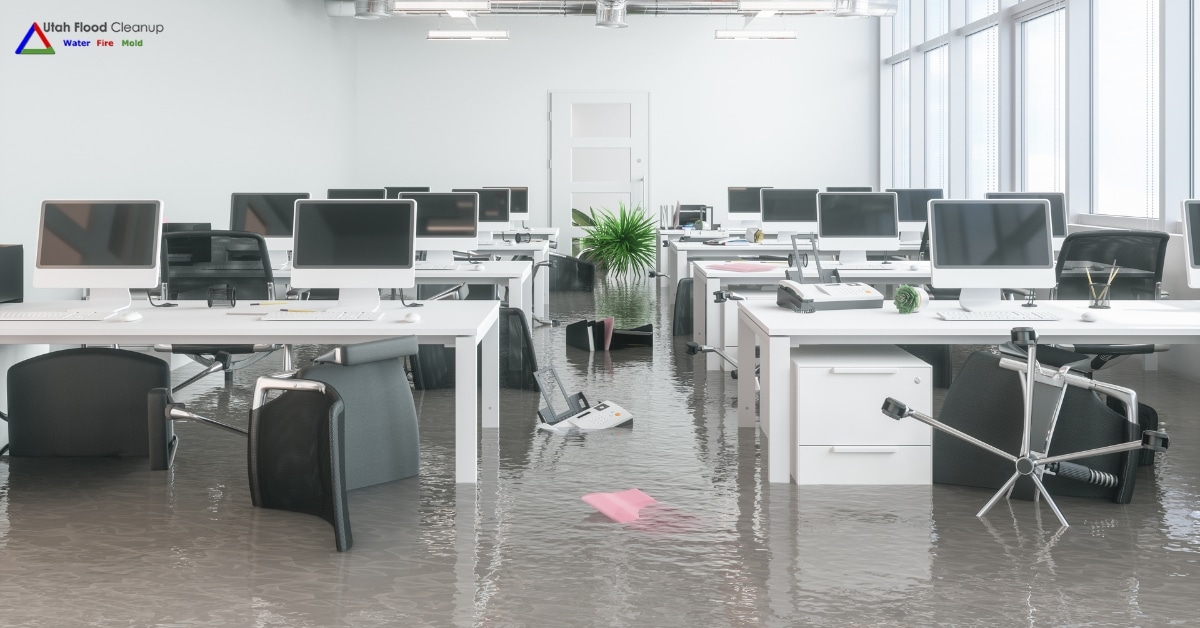
"Smoke" refers to a mix of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases produced when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis. It's typically accompanied by quantities of air that are entrained or blended into the mass. Smoke often results from fires, including household fires from stoves, candles, oil lamps, and fireplaces. It's also utilized in practices such as pest control (fumigation), communication (smoke signals), military operations (smoke screens), cooking, and various smoking activities. In certain rituals, substances like incense, sage, and resin are burned to generate smoke for spiritual purposes. Moreover, smoke serves as a flavoring agent and preservative in some foods and is a component of internal combustion engine exhaust gas, notably diesel exhaust. Smoke inhalation can pose serious health risks, including thermal damage, poisoning, and pulmonary irritation due to harmful combustion products, making it the primary cause of death in indoor fire incidents. The particles in smoke form an aerosol that effectively scatters visible light, creating an effect similar to textured privacy glass.
Utah Flood Cleanup
Latest posts by Utah Flood Cleanup (see all)
- From Ashes to Home Sweet Home: Fire and Smoke Damage Restoration in Utah - December 20, 2023
- Thanksgiving Safety: An Essential Guide to the Leading Causes of Home Fires - November 17, 2023
- Complete Water Damage Repair: Why Salt Lake City Trusts Utah Flood Cleanup - November 15, 2023